第 6 章 数组、排序和查找
Suriski 9/6/2022 韩顺平java笔记
- 韩顺平 2021零基础学Java的笔记,可在Bilibili同步观看
- 韩顺平-视频观看地址 (opens new window)
# 6.1 为什么需要数组
# 6.1.1 数组介绍

# 6.1.2 数组快速入门
可以通过 数组名.length 得到数组的大小/长度
# 6.2 数组的使用

注意:int a[ ] = new int [5] 和 int[ ] a = new int [5] 是等价的。
# 6.2.1 使用方式 2-动态初始化

# 6.2.2 使用方式 3-静态初始化

# 6.3 数组使用注意事项和细节

# 6.5 数组赋值机制

# 6.6 数组拷贝


# 6.7 数组反转

方式 1:通过找规律反转
public class ArrayReverse {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {11, 22, 33, 44, 55, 66};
int temp = 0;
int len = arr.length;
for( int i = 0; i < len / 2; i++) {
temp = arr[len - 1 - i];
arr[len - 1 - i] = arr[i];
arr[i] = temp;
}
System.out.println("===翻转后数组===");
for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + "\t");
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
方式 2:使用逆序赋值方式
public class ArrayReverse02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {11, 22, 33, 44, 55, 66};
int[] arr2 = new int[arr.length];
for(int i = arr.length - 1, j = 0; i >= 0; i--, j++) {
arr2[j] = arr[i];
}
arr = arr2;
System.out.println("====arr 的元素情况=====");
for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + "\t");
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
# 6.9 排序的介绍

# 6.10 冒泡排序法
冒泡排序(Bubble Sorting)的基本思想是:通过对待排序序列从后向前(从下标较大的元素开始),依次比较相邻元素 的值,若发现逆序则交换,使值较大的元素逐渐从前移向后部,就象水底下的气泡一样逐渐向上冒。


public class BubbleSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {24, 69, 80, 57, 13, -1, 30, 200, -110};
int temp = 0;
for( int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++) {
for( int j = 0; j < arr.length - 1 - i; j++) {
if(arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) {
temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j+1];
arr[j+1] = temp;
}
}
System.out.println("\n==第"+(i+1)+"轮==");
for(int j = 0; j < arr.length; j++) {
System.out.print(arr[j] + "\t");
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
# 6.12 查找
# 6.12.1 介绍:
在 java 中,我们常用的查找有两种:
- 顺序查找
- 二分查找
# 6.12.2 案例演示:
有一个数列:白眉鹰王、金毛狮王、紫衫龙王、青翼蝠王猜数游戏:从键盘中任意输入一个名称,判断数列中是否 包含此名称【顺序查找】 要求: 如果找到了,就提示找到,并给出下标值。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class SeqSearch {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] names = {"白眉鹰王", "金毛狮王", "紫衫龙王", "青翼蝠王"};
Scanner myScanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入名字");
String findName = myScanner.next();
int index = -1;
for(int i = 0; i < names.length; i++) {
if(findName.equals(names[i])) {
System.out.println("恭喜你找到 " + findName);
System.out.println("下标为= " + i);
index = i;
break;
}
}
if(index == -1) {
System.out.println("sorry ,没有找到 " + findName);
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
# 6.14 二维数组的使用
# 6.14.2 使用方式 1: 动态初始化

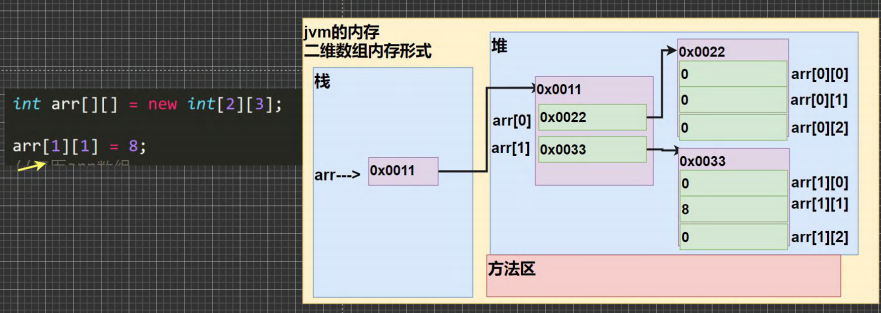
# 6.14.3 使用方式 2: 动态初始化

# 6.14.4 使用方式 3: 动态初始化-列数不确定
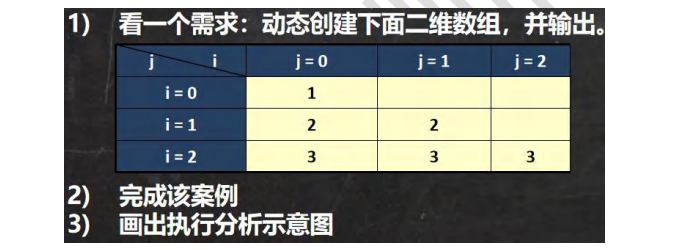
public class TwoDimensionalArray03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] arr = new int[3][];
for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] = new int[i + 1];
for(int j = 0; j < arr[i].length; j++) {
arr[i][j] = i + 1;
}
}
System.out.println("=====arr 元素=====");
for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < arr[i].length; j++) {
System.out.print(arr[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
# 6.14.5 使用方式 4: 静态初始化

# 6.15 二维数组的应用案例
使用二维数组打印一个 10 行杨辉三角

public class YangHui {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] yangHui = new int[12][];
for(int i = 0; i < yangHui.length; i++) {
yangHui[i] = new int[i+1];
for(int j = 0; j < yangHui[i].length; j++){
if(j == 0 || j == yangHui[i].length - 1) {
yangHui[i][j] = 1;
} else {
yangHui[i][j] = yangHui[i-1][j] + yangHui[i-1][j-1];
}
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < yangHui.length; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < yangHui[i].length; j++) {
System.out.print(yangHui[i][j] + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
# 6.16 二维数组使用细节和注意事项

# 6.17 二维数组课堂练习

